The Chézy equation, also known as the Chézy formula, is a fundamental equation in fluid dynamics used to calculate flow velocity and rate in open channels. Attributed to French engineer Antoine de Chézy, this equation describes the relationship between flow velocity, Chézy coefficient, hydraulic radius, and slope.

In this article, we will delve into the components of the Chézy equation, including the Chézy coefficient, modifications to the equation, and its limitations and assumptions.
Understanding the Chezy Equation
The Chézy equation, also commonly known as the Chézy formula, attributed to French engineer Antoine de Chézy, was first introduced in 1768 as an attempt to describe the complex behavior of fluid flow in open channels. Chézy discovered that the flow velocity in a channel constituted a significant factor in determining its capacity to transport water.
The Chézy equation can be expressed as:
Elevate Your Engineering With Excel
Advance in Excel with engineering-focused training that equips you with the skills to streamline projects and accelerate your career.
Find Out More

Where:
- V = flow velocity [m/s]
- C = Chézy coefficient [m1/2/s]
- Rh = hydraulic radius [m]
- S = slope of the energy grade line [unitless]
To calculate for the flow rate, the above formula can be transformed as follows:

Where:
- Q = flow rate [m3/s]
- A = cross-sectional area of the flow [m2]

In uniform open channel flow, the slope of the energy grade line is equal to the slope of the channel bed as well as the slope of the water surface. According to the Chezy formula, increasing the channel inclination and hydraulic radius results in higher flow velocity.
The Chezy coefficient ranges typically from30 m1/2/s to 90 m1/2/s. Its value depends on the channel roughness. That is, a smoother channel surface enhances the flow velocity compared to a rough surface.
The hydraulic radius Rh can be calculated as:

Where:
- A = cross-sectional flow area [m²]
- P = wetted perimeter [m]
The wetted perimeter is the contact length between the channel’s flowing liquid and the channel’s boundary.
The Chezy Coefficient
For many years after the development of the formula, the Chezy coefficient was believed to be constant— unaffected by flow conditions. However, further research demonstrated that the coefficient depends on both the Reynolds number and channel roughness.
The Chezy coefficient can be determined experimentally or estimated using different empirical formulas, such as the Ganguillet Kutter Formula and the Bazin Formula.
Ganguillet Kutter Formula
The Ganguillet Kutter Formula for calculating the Chezy coefficient can be expressed as:

Where:
- n = Kutter’s roughness coefficient [unitless]
Note that the above formula is only applicable for SI units. For imperial units, the following equation can be used:

Bazin Formula
Alternatively, Bazin Formula can be used to calculate for the Chezy coefficient. In SI units, it can be expressed as:

Where:
- m = Bazin’s constant [unitless]
In imperial units, it can be written as:

The table below lists the value of Bazin’s constant for some common open channels.
Modifications to the Chezy Equation
Over time, engineers and mathematicians proposed modifications to the Chezy equation to enhance its accuracy and applicability to evolving fluid dynamics challenges. One example is the Manning equation developed by Irish engineer Robert Manning.
The Manning equation improved upon Chézy’s equation by providing a more accurate representation of the connection between hydraulic radius and velocity. It also replaced the empirical Chézy coefficient (C) with the Manning roughness coefficient (n).
Unlike the Chézy coefficient, which needed to be determined through field measurements, the Manning coefficient was found to be constant based on the material of the wetted perimeter. This enabled the creation of a standardized table of values for reasonably estimating flow velocity.
In SI units, the Manning equation can be expressed as:
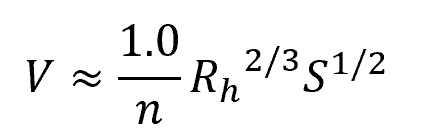
Where:
- n = Manning’s roughness coefficient [unitless]
In imperial units:

The Chezy coefficient can also be related to Manning’s roughness coefficient using the following equation:

Limitations and Assumptions
The Chézy equation assumes that the flow is uniform and under steady-state conditions. It is mainly suitable for rectangular channels and open channel flows, and may not provide accurate results for other channel shapes, such as trapezoidal channels. In such cases, alternative equations may be more appropriate.

Furthermore, the Chézy equation does not consider energy losses caused by turbulence, wave action, or boundary shear stress. It only takes into account channel roughness, hydraulic radius, and bed slope. It assumes an idealized, laminar flow, which may not reflect the actual behavior of fluid flow, especially in channels with complex geometries or rapidly changing flow conditions.
It is important to be aware of these limitations and assumptions when interpreting results or applying the Chezy equation to practical situations. Ultimately, it essential to thoroughly examine the reality of the channel and flow conditions and explore additional equations or methods when necessary.
Example Problem
Problem: A rectangular channel has a base (B) of 4 meters and a height (H) of 2 meters. If it is inclined at a slope of 0.002, calculate the flow velocity and flow rate along the channel. Assume a Chezy coefficient of 50 m1/2/s.
Solution: First, let’s calculate for the hydraulic radius:

Now, let’s use the Chezy equation to calculate for the flow velocity:

Multiple the above equation by the flow area to get the flow rate as follows:

Therefore, the velocity of the flow along the channel is 2.24 m/s and it is flowing at a volumetric rate of 17.89 m3/s.